If you’ve been following OpenSnow’s Bryan Allegretto for his Lake Tahoe forecasts, you know he’s passionate about accurately predicting what the surrounding mountains will get. He’s the voice of reason when other news outlets and weather services hype up FEET of snow, only for the reality to fall far short. But even for “BA”—as he’s known—the storms in the first week of February 2025 were way off, and by a huge margin. In fact, it was his worst prediction in his nineteen-plus-year career. I had the chance to chat with him to get the inside scoop on what went wrong.
BA’s Soul Crushed

BA takes his forecasting seriously—so seriously that he’s been keeping a scorecard to track just how spot-on (or not) he’s been. Over the past nine seasons, his predictions for every storm across the Tahoe Basin have been off by just 1.5 inches on average. But during the first week of February, things went way off course. He was off by anywhere from 5.5 to 12.9 inches, with some mountains missing the mark by as much as 2 feet! Normally, when he’s that far off, it’s because the storms delivered more (think: colder, fluffier powder). This time? As far as he can remember, it was the first instance they delivered way less.
Atmospheric Rivers are Tough

Lake Tahoe’s weather is infamous for its feast-or-famine cycles, and a big reason is that up to 50% of California’s precipitation comes in the form of an atmospheric river. These intense bands of moisture originate from the tropics and slam into the Sierra. If Lake Tahoe is lucky enough to be on the cold side of it, we get huge snowfall. But if not, it means rain—LOTS of rain. And that’s exactly what happened during the first week of February.
Alarm Bells Ding
As the storms began to arrive in the 5-day window, BA was already mentioning how concerned he was about the forecast. First, the band of moisture was narrow at only 50 miles wide which is tiny in the scope of the globe. If the storm moved even a few miles north or south, the amount of liquid we get would be drastically cut. Then there was the problem of temperatures. It set up a battle royale of two giants – cold air to the north and the warm subtropical air flowing into the northern Sierra. Depending on who wins and when, this “could make a BIG difference in snowfall totals.”
Worst Case Scenario Happened
And that’s exactly what happened. Instead of the storm staying focused on Tahoe, it quickly moved north. While the National Weather Service predicted 30 inches of liquid and BA estimated 22 inches as a conservative forecast for the week, the greater Lake Tahoe area only received a meager 6-12+ inches. The moisture tap shut off before the cold air could move in, and the snow ratios—usually around 10:1—were closer to 7:1. The result? A rude awakening after the storm passed.
“Biggest Temperature Gradients as Far as I Can Remember”
A lot of this came down to how cold it was to the north—a real tease for weather forecasters. It was snowing all the way to the beach in Oregon and even in Susanville. With that much cold air up north, it seemed like it would force its way south, but it didn’t. Instead, the warm air took over. Not just in Tahoe, but across the entire West, where everyone got hit with rain. Jackson Hole was in the 50s, and even Utah saw rain!
Models Aren’t Gospel but a Tool
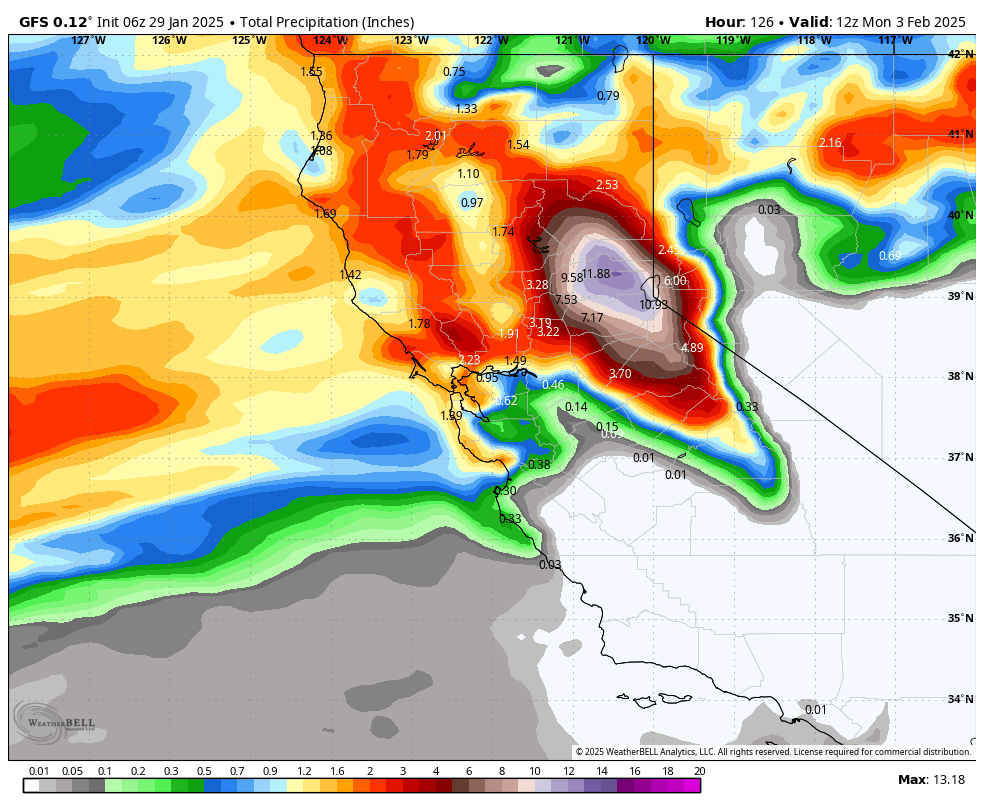
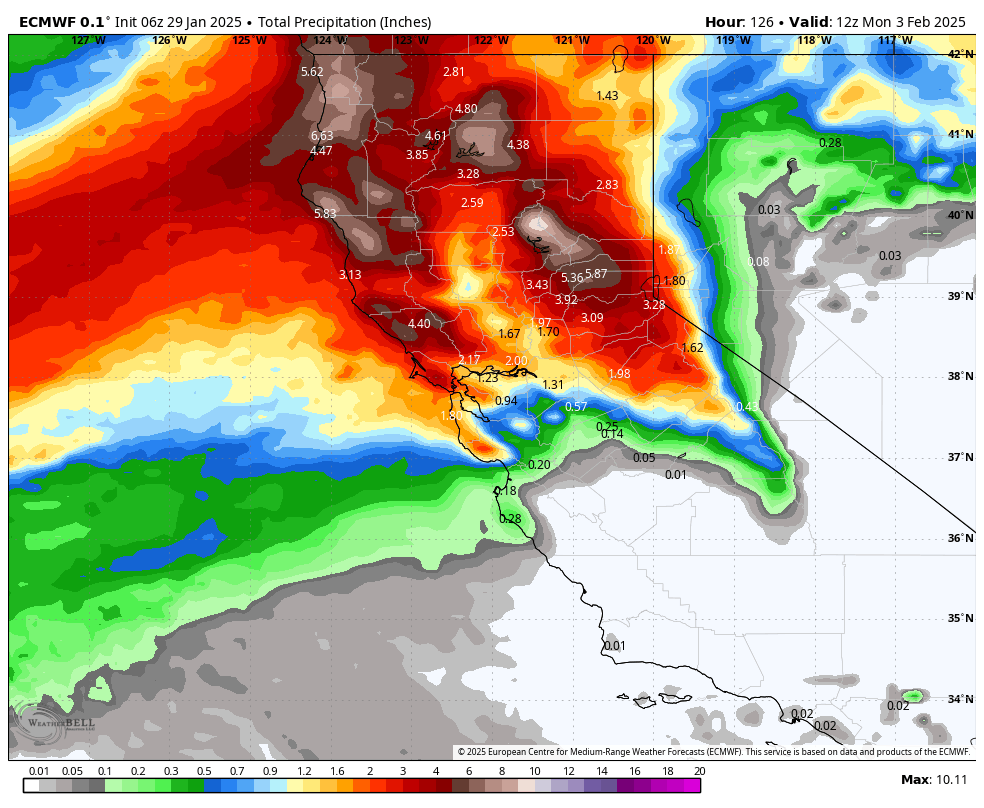
The best tool for weather forecasters today is still the weather models. But as BA pointed out, “These are global models. Each micro-climate has its own set of errors. You need to understand these nuances and apply them to your forecast.” Take the GFS, for example. The U.S. model, affectionately known as “snow porn,” always assumes snow ratios are way too high, predicting crazy amounts of snow—and it’s nearly always wrong. Then there’s the Canadian model, which tends to underforecast how much snow places like Mt. Rose will get. The real voice of reason? The European model. Statistically, it’s proven to be the most accurate, and now with A.I. to help fix its errors, it’s getting even better.
OpenSnow Will Learn and Get Better
In the end, BA summed it up best: “It’s hard to forecast storms in the mountains.” But that’s exactly what drew Bryan to this field in the first place—the challenge of forecasting and getting it right. Sometimes, like the week of February 1st, 2025, you get it wrong. But that’s an outlier, and the team at OpenSnow is using it as a learning tool. Instead of taking a back seat, they’re constantly working to improve their product. They’ve even hired a full-time A.I. developer to create their own OpenSnow A.I., which is processing 40+ years of data to correct model errors and improve predictions.
And it’s not all about enjoying the summer for pickleball. The folks at OpenSnow use the “off season” as a chance to reflect and improve. That’s when they discovered the Canadian model’s issue with the Mt. Rose snow forecast. They’re always striving to get better.
We get how tough forecasting can be, and we hope this behind-the-scenes look helps explain the challenges involved. Big kudos to him—and to all of the OpenSnow team—for the hard work they put in!











We love you BA! That’s why it’s called a forecast and not the exact truth of what’s going to happen.
“You can’t control the weather, you can only control your attitude about it”
~Palacio Proverb
Good proverb!